Many people who experience a slipped or herniated spinal disc will have few or no symptoms. Bed rest and, if there is pain, analgesics and anti-inflammatory medication are usually enough to resolve the problem within about six weeks. But for the unlucky few - statistics range from one in 10 to one in 100 -going under the knife is the only way to solve the problem.
You have 23 discs in your spine, which is surrounded by a complex network of nerves, muscles, tendons and ligaments.
Additional factors are smoking, being overweight and having a job that involves a lot of sitting (including driving and sitting in front of a computer). Genes also play a part.
Lumbar (or lower-back) disc herniation is more common than the cervical (or upper-back) kind.
The term slipped disc is somewhat misleading in that a disc cannot actually slip out of place.
Other symptoms of a herniated disc are numbness or tingling in the limbs and/or weakness in the muscles. In some people, the referred neural pain of a slipped disc is so intense that it becomes impossible for them to sit, walk or lie in certain positions.
The first six weeks following surgery are critical to healing; the first three months are important; and it can take up to a year for the healing process to be complete.
What is a Disc?
A vertebral disc is the protective, circular pad of cartilage that lies between each vertebra of your spine. The disc is made up of a tough, fibrous outer casing with a softer, gel-like substance inside. Your discs hold your vertebrae together and cushion and protect them when you jump or run.You have 23 discs in your spine, which is surrounded by a complex network of nerves, muscles, tendons and ligaments.
What Causes Disc Degeneration?
Our discs degenerate as we get older: they start to lose their water content, causing them to dehydrate and making them less flexible and more prone to damage. But a slipped or herniated disc can also be caused by an injury such as a fall, by bending awkwardly, and by pushing, pulling or lifting heavy objects.Additional factors are smoking, being overweight and having a job that involves a lot of sitting (including driving and sitting in front of a computer). Genes also play a part.
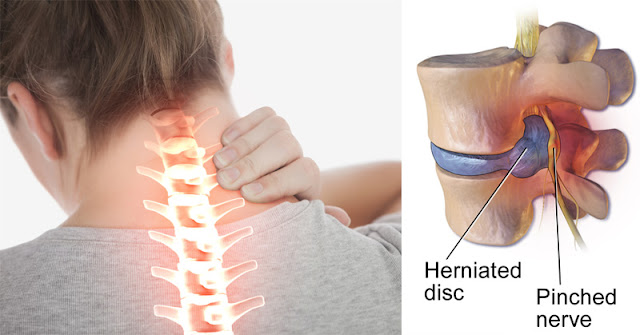
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated or slipped disc is a disc whose outer casing has torn, allowing the gel inside to bulge out. The protruding matter may press on any of the many nerves that surround the spine, causing varying degrees of discomfort and pain.Lumbar (or lower-back) disc herniation is more common than the cervical (or upper-back) kind.
The term slipped disc is somewhat misleading in that a disc cannot actually slip out of place.
Who is Likely to Experience a Herniated Disc?
More men than women have this problem, and it affects mainly people over the age of 30.There is also a strong genetic component: people with a family history of back problems are more prone to the disorder. It is also more likely to happen to people who have jobs that involve long periods of sitting or heavy lifting (especially if a heavy object is lifted while the person is bent at the waist rather than with bent legs and a straight back) - but it can happen to anyone at any time.How Does a Slipped Disc Manifest?
Slipped discs most often happen in the lower back but, oddly enough, this isn’t always where you feel the pain – and, in fact, some people may experience no pain or discomfort at all. The referred pain of a slipped disc happens when the protruding part presses on any of the nerves around the spine, particularly the very large sciatic nerve, causing pain in the buttocks, legs and feet (or, if the damaged disc is higher in the back, in the neck, arms and hands). Muscle spasm is sometimes a symptom of a slipped disc.Other symptoms of a herniated disc are numbness or tingling in the limbs and/or weakness in the muscles. In some people, the referred neural pain of a slipped disc is so intense that it becomes impossible for them to sit, walk or lie in certain positions.
How is a Slipped Disc Diagnosed?
Initially, your GP will do a few simple tests, including testing your reflexes, walking ability and muscle strength. Most herniated discs heal themselves over about six weeks. If, however, the pain persists or other symptoms present themselves (most seriously, bladder or bowel problems as a result of nerve interference), you’ll need to have an X-ray to rule out the possibility of a tumour, infection or fracture. These excluded, an MRI will determine the extent of the damage caused by a herniated disc.What are the Treatment Options for a Slipped Disc?
Bed rest and medication (including prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatories) usually do the trick, and therapy by a physiotherapist or chiropractor can help. Surgery is always a last resort when it comes to a herniated disc. Various specialists cite stats ranging from nine in 10 to 99 in 100 people whose problem will resolve without it – but for that unlucky small percentage, surgery is the only way to go. Unfortunately, however, even the surgery doesn’t always work for some people, who might still require further medical treatment after an operation.What Does a Discectomy Involve?
For a discectomy, the surgeon will need reference to an MRI to see exactly what needs to be done. The operation is done under general anaesthetic and takes 60-90 minutes, depending on what is involved. Once you have been put under, the surgeon will make a small incision in your back and remove the bulging parts of the damaged disc or the entire disc.How Long Does it Take to Recover from a Discectomy and What is Involved?
Recovery rates vary depending on the age, health and attitude of the person who’s had the operation. Although sitting is very restricted for the first two weeks and driving for the first three, you do need to get active as soon as you can. You will be given a light exercise regime by your doctor, which you must follow, and you should go for a walk every day.The first six weeks following surgery are critical to healing; the first three months are important; and it can take up to a year for the healing process to be complete.